The Future of Supply Chain: Innovations, Challenges, and Strategic Solutions
Advanced robotics, AI-powered decision-making systems, and strategic alliances are driving a radical change in the supply chain environment. Logistics networks are becoming more robust, sustainable, and efficient as a result of these advancements. Leading the way in this evolution is MacMillan Supply Chain Group, which uses state-of-the-art technologies and builds cooperative partnerships to maximize the flow of goods across borders and throughout Canada. This article examines how supply chains are changing as a result of these developments and how companies can use them to their advantage in a market that is becoming more and more complex.
Introduction
The world of supply chains is evolving more quickly than in the past. What used to involve a lot of manual labor, paper records, and reactive problem-solving is now being automated, digitalized, and proactive. We at MacMillan Supply Chain Group are seeing directly how the transportation of goods from producers to customers is being transformed by robotics, artificial intelligence, and strategic alliances.
Large geographic distances, complicated cross-border relations with the US, and seasonal weather extremes that can cause logistical disruptions are some of the particular difficulties faced by Canadian businesses. Supply chain management in the future tackles these issues by fostering cooperative partnerships and technological advancements that build stronger networks.
Understanding these new trends is essential for retailers, manufacturers, and distributors to stay competitive in the quick-paced market of today. Let’s examine how intelligent strategies, robust partnerships, and robots are constructing tomorrow’s supply chains.
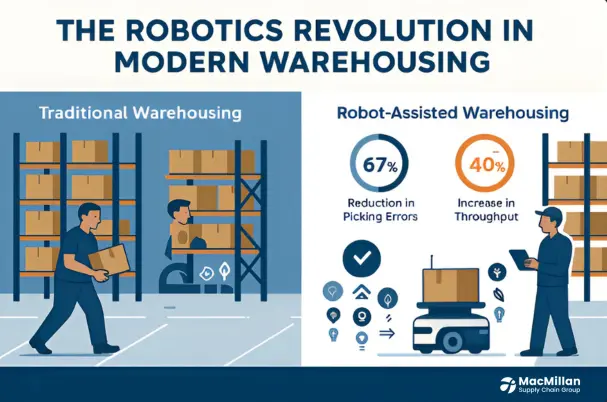 Robotics Revolution in Warehouse Operations
Robotics Revolution in Warehouse Operations
Robotics in logistics is bringing about a technological renaissance on the warehouse floor. These days, autonomous mobile robots, or AMRs, move inventory and help human workers by precisely navigating warehouse aisles. These robots significantly boost productivity in the Ontario logistics hub and beyond by avoiding obstacles and optimizing their routes using advanced sensors and artificial intelligence.
Warehouse automation has increased throughput by 40% and decreased picking errors by almost 67% at MacMillan Supply Chain Group. These enhancements focus on consistency and dependability rather than just speed. No matter the time of day, robots perform at the same level, never get tired, and never require breaks.
In contemporary warehousing, human-robot collaboration is the sweet spot. Instead of taking the place of employees, robots perform physically taxing, repetitive tasks while humans concentrate on intricate decision-making and quality assurance. Collaborative picking systems, for instance, pair humans with robots; the human chooses items that need judgment and dexterity, while the robot moves bins.
In Canada, industrial automation is growing, especially as companies continue to face labor shortages. By operating in areas with less heating and lighting, automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS) can maximize vertical storage space while lowering energy expenses. In cities where warehouse space is scarce, this efficiency is especially beneficial.
Big businesses are not the only ones embracing the robotics revolution. Mid-sized companies can now use this technology thanks to scalable solutions, which enables them to compete with bigger players in the logistics industry, which is becoming more and more technologically advanced.
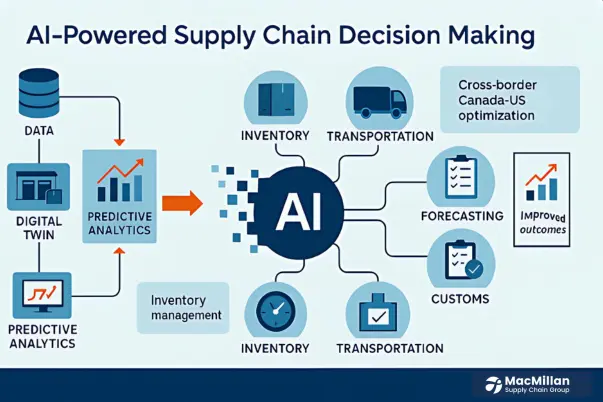
AI-Driven Supply Chain Decision Making
Artificial intelligence has developed from simple automation to a tool for strategic decision-making in modern supply chains. Large volumes of data are used by the AI-powered supply chain to forecast interruptions, optimize inventory levels, and improve customer service. Human analysts are unable to process information at the speed and scale that this technology can.
The foundation of this revolution is predictive analytics. Artificial intelligence (AI) systems can predict demand with remarkable accuracy by examining historical data as well as external factors like weather patterns, economic indicators, and social media trends. This entails minimizing stockouts and excess inventory by having the appropriate products in the right quantities at the right locations for a retailer getting ready for the holidays.
Another innovation in supply chain management is the use of digital twins. Businesses can model changes and disruptions before they happen with these virtual versions of real supply chains. Businesses can minimize risk and maximize results by testing scenarios in the digital environment before deciding on new warehouse layouts or transportation routes.
These technologies are used by MacMillan Supply Chain Group to build robust supply chain networks for our customers. Our AI systems swiftly recalculate the best routes and resource allocations in the event of unforeseen circumstances, such as snowstorms or border delays. Your customers will experience fewer disruptions as a result of this proactive approach.
The impact of AI extends to cross-border trade between Canada and the US as well. Machine learning algorithms can predict customs clearance times, recommend optimal shipping methods, and even anticipate tariff impacts before they affect your bottom line. International logistics are turned from a source of uncertainty to a strategic advantage thanks to this intelligence.
 Creating Strategic Alliances in the Supply Chain
Creating Strategic Alliances in the Supply Chain
Relationships are more important to supply chain management in the future than technology alone. Across the supply chain ecosystem, transactional interactions are giving way to strategic partnerships. Beyond just purchasing and selling, these cooperative partnerships add value.
These collaborations are becoming more transparent than ever thanks to blockchain technology. All supply chain participants have access to a single, unchangeable record of transactions and movements thanks to blockchain technology. Disagreements regarding delivery schedules, product quality, and contractual duties are resolved by this common truth. For businesses engaged in cross-border trade between Canada and the US, this transparency reduces delays and administrative burdens.
Successful supply chain strategy now depends on collaboration rather than competition. When manufacturers, logistics providers, and retailers align their systems and share data, the entire network becomes more efficient. At MacMillan Supply Chain Group, we facilitate these connections, helping businesses build integrated supply chains that respond quickly to changing market conditions.
The benefits of strategic partnerships extend to sustainability in logistics as well. By coordinating transportation and sharing warehouse space, companies can reduce their carbon footprints while cutting costs. These green supply chain initiatives satisfy growing consumer demand for environmental responsibility while improving operational efficiency.
The most successful businesses are those that view their logistics providers not as vendors but as strategic partners. This mindset shift opens opportunities for innovation, cost reduction, and competitive advantage that transactional relationships simply cannot deliver.
Sustainability and the Green Supply Chain
Sustainability is evolving from a desirable attribute to a business necessity as environmental concerns shift supply chain priorities. Reducing carbon emissions, minimizing packaging waste, and putting circular economy principles into practice are all included in the green supply chain concept.
Electric delivery vehicles are becoming more and more popular in Canada, according to supply chain trends, especially for last-mile logistics in cities. These cars use less fuel and require less maintenance, which lowers emissions and frequently lowers operating costs. We at MacMillan Supply Chain Group are assisting customers in making the switch to these more environmentally friendly modes of transportation without compromising on dependability or efficiency.
Energy-efficient heating, cooling, and lighting systems are also making warehouse operations more ecologically friendly. Automated systems can work in environments with less light and temperature control, which further saves energy. Instead of following set schedules, smart building management systems optimize resource use based on actual needs.
Another frontier in supply chain sustainability is packaging. Waste reduction is facilitated by biodegradable materials, reusable shipping containers, and appropriately sized packaging. These programs frequently lower material costs while also satisfying consumer preferences for companies that practice environmental responsibility.
By creating systems where materials and products are recycled, refurbished, or reused at the end of their lifecycle, the circular supply chain concept goes even farther in promoting sustainability. This strategy necessitates tight collaboration between producers, logistics companies, retailers, and customers—exactly the kind of strategic alliances that will shape supply chain management in the future.
Typical Issues with the Supply Chain of the Future
Businesses encounter major implementation and adaptation challenges in spite of the encouraging developments in supply chain technology and strategy. When trying to integrate new technologies with legacy systems, integration issues frequently come up. Many businesses still use warehouse management systems (WMS) that are decades old, which makes them incompatible with contemporary robotics and artificial intelligence (AI) technologies.
Another significant obstacle is the skills gap. Workers require new technical skills to program, maintain, and work together with warehouse automation and AMR technology as these technologies become more common. Finding and retaining talent with these skills remains difficult, particularly in competitive job markets.
Cybersecurity issues are brought up by supply chains becoming more and more digital. Despite being designed to be secure, blockchain solutions still require proper implementation and management, and linked systems present additional security risks. Whole supply chain networks can be jeopardized by data breaches, not just a single business.
Regulatory compliance presents an additional level of complexity for Canadian companies that trade internationally with the US. Rapid changes in tariff effects necessitate quick thinking and a thorough comprehension of international trade regulations. Without specialized knowledge, smaller businesses usually struggle to meet these demands.
Small and medium-sized businesses face obstacles to entry due to the high initial investment costs associated with robotics and AI systems. Even though the long-term return on investment might be strong, the initial capital outlay might be too high, which could cause the gap between big businesses and their smaller rivals to grow.
Last but not least, perceived costs and implementation difficulties frequently lead to opposition to sustainability initiatives. Coordination between several organizations, each with their own priorities and limitations, is necessary to create supply chains that are truly green. These initiatives may stall or produce less than ideal results if incentives are not aligned.
 Our Solutions
Our Solutions
We at MacMillan Supply Chain Group have created all-encompassing strategies to deal with these typical issues in the changing supply chain environment. Our solutions assist companies in navigating the intricacies of contemporary logistics by fusing technology, knowledge, and cooperative tactics.
We provide modular implementation of new technologies that can coexist with current systems in order to overcome integration challenges. With our phased approach, companies can implement AI-powered supply chain solutions and robotics in logistics without interfering with ongoing business operations. We offer middleware solutions that build a bridge between new capabilities and legacy warehouse management systems by connecting them with state-of-the-art automation tools.
Our extensive training programs and knowledge transfer initiatives help to close the skills gap. We do more than just install equipment when deploying AMR or warehouse automation; we also build your team’s capabilities. Our training ensures your staff can optimize the value of these investments by covering both technical operation and strategic utilization of new systems.
We use multi-layered protection protocols at every digital supply chain touchpoint to address cybersecurity concerns. Advanced encryption and access controls are features of our blockchain solutions, and our systems are regularly updated and subject to security audits. We maintain dedicated cybersecurity specialists who monitor emerging threats and develop countermeasures before they can impact your operations.
Our expertise in cross-border trade between Canada and the US helps clients navigate regulatory complexities with confidence. We maintain current knowledge of customs requirements, tariff impacts, and international shipping regulations. Our predictive analytics tools forecast potential compliance issues before they arise, allowing proactive adjustments to shipping strategies.
To make advanced technology accessible to businesses of all sizes, we offer flexible engagement models including technology-as-a-service options. These arrangements convert large capital expenditures into manageable operational costs, allowing smaller companies to access the same advanced capabilities as larger competitors. Our scalable solutions offer the appropriate degree of assistance at every stage of your development, growing with your company.
Our efforts to improve logistics sustainability benefit the environment and increase operational effectiveness. Through shared transportation resources that maximize vehicle utilization, packaging optimization that minimizes waste, and optimized routing that lowers fuel consumption, we assist clients in implementing green supply chain practices. These methods cut expenses and lessen their negative effects on the environment.
Through digital twins and simulation modeling, we help clients test new strategies before full implementation. This approach reduces risk and increases confidence in new initiatives, whether you’re redesigning warehouse layouts, implementing new automation systems, or developing more resilient supply chain networks.
We work together to establish strategic alliances across your supply chain. By fostering relationships between businesses that complement one another, we open doors for resource sharing, cooperative planning, and reciprocal development. In ways that isolated operations cannot, these partnerships improve resilience and generate competitive advantages.
MacMillan Supply Chain Group provides comprehensive solutions to the problems that contemporary supply chains face by fusing technological innovation with real-world knowledge and cooperative tactics. Our integrated strategy guarantees that developments in sustainability, artificial intelligence, and robotics result in real business advantages for our clients.
How to Implement Future Supply Chain Solutions
A strategic approach that strikes a balance between innovation and pragmatic realities is necessary for the implementation of advanced supply chain solutions. Begin by thoroughly evaluating your current operations to pinpoint specific problems and areas that could use improvement. This foundational knowledge will assist you in setting investment priorities and tracking outcomes.
Instead of trying a complete transformation, create a plan for a phased implementation. To test new technologies and procedures without upsetting your entire business, start with pilot projects in controlled settings. Before implementing AMR technology throughout your entire facility, for instance, start with a single warehouse section.
Invest in your team’s capabilities alongside technology investments. The most sophisticated warehouse automation systems will underperform without properly trained staff. Create dedicated training programs and consider hiring specialists who can bridge the gap between traditional logistics knowledge and emerging technologies.
Give preference to technology partners with industry-specific experience and integration expertise. The ideal partner will be aware of your operational environment’s realities as well as the potential of new systems. We apply this dual viewpoint to every client interaction at MacMillan Supply Chain Group, guaranteeing solutions that function in practical settings.
Build data collection and analysis capabilities early in your transformation journey. AI-powered supply chain solutions depend on quality data, so establish systems to capture relevant information from throughout your operations. Clean, consistent data provides the foundation for predictive analytics and digital twins that drive strategic decision-making.
Don’t undervalue the significance of change management. Workflows and mindsets must be modified to accommodate new technologies and procedures. To create momentum, explain the change’s justifications in detail, include frontline staff in the planning stages, and acknowledge early victories.
When it comes to supply chain transformation, think about collaborating with MacMillan Supply Chain Group. We are in a position to assist you in navigating the technological and regulatory complexities of cross-border trade with the United States and Canadian supply chain trends. We provide comprehensive solutions that tackle your unique problems and set up your company for future expansion.
Get in touch with us right now to find out how we can assist you in putting the supply chain tactics and technologies that will propel your company forward into action. Together, you and our team of professionals will create a tailored strategy that creates long-term competitive advantages and yields immediate benefits.
FAQS
Robotics in logistics delivers multiple benefits including increased accuracy (typically reducing errors by 60-70%), improved throughput (often 30-50% higher than manual operations), enhanced safety (reducing workplace injuries), and consistent performance regardless of time of day or staffing challenges. At MacMillan Supply Chain Group, we've helped clients achieve these improvements while maintaining flexibility to handle changing business requirements.
AI-powered supply chain systems analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and make predictions that human analysts might miss. These systems can forecast demand with greater accuracy, optimize inventory levels to reduce carrying costs, predict potential disruptions before they occur, and automatically adjust routing and resource allocation in response to changing conditions. The result is more proactive management and fewer costly surprises.
Cross-border trade faces challenges including fluctuating customs clearance times, changing regulatory requirements, tariff impacts that can alter cost structures, and documentation complexities. Weather conditions along northern routes can create seasonal disruptions, while differing holidays and business practices add another layer of complexity. MacMillan Supply Chain Group specializes in navigating these challenges through expertise, technology, and established relationships with border agencies.
Small businesses can leverage technology-as-a-service models that convert capital expenses to operational costs, implement modular solutions that address specific pain points rather than complete systems, and partner with 3PL providers like MacMillan Supply Chain Group that offer advanced capabilities without requiring direct investment. Cloud-based systems have also made sophisticated supply chain management tools more accessible to businesses of all sizes.
Begin by measuring your current environmental impact, including transportation emissions, energy usage, and packaging waste. Identify quick wins like optimizing delivery routes to reduce fuel consumption, right-sizing packaging to minimize material use, and consolidating shipments to maximize vehicle utilization. Partner with logistics providers that offer green transportation options and sustainable warehouse operations, such as MacMillan Supply Chain Group's energy-efficient facilities.
Digital twins create virtual replicas of your physical supply chain, allowing you to simulate changes and test scenarios without disrupting actual operations. This capability enables you to optimize warehouse layouts, test new routing strategies, evaluate different inventory policies, and prepare for potential disruptions. The insights gained from these simulations lead to more confident decision-making and reduced implementation risks.
Blockchain solutions provide immutable, transparent records of transactions and movements throughout the supply chain. This technology enables all parties to access a single version of truth, reducing disputes and administrative burden. Blockchain can verify product authenticity, track ethical sourcing compliance, streamline customs documentation, and facilitate automated payments through smart contracts. These capabilities build trust between partners while improving operational efficiency.
The Ontario logistics hub is increasingly adopting warehouse automation, AMR technology, and AI-powered management systems to address labor challenges and growing e-commerce demands. Its strategic location for cross-border trade between Canada and the US makes it a focal point for technology investment. MacMillan Supply Chain Group maintains significant operations in this region, leveraging its connectivity and skilled workforce to deliver advanced logistics solutions.
Tomorrow's supply chain professionals will need a combination of technological literacy, analytical thinking, and relationship management capabilities. Understanding how to interpret data from predictive analytics systems, collaborate with automated systems, and optimize human-robot collaboration will be crucial. Equally important will be the ability to build and maintain strategic partnerships across organizational boundaries. MacMillan Supply Chain Group invests in developing these skills within our team.
Measure ROI by tracking specific metrics before and after implementation, including order accuracy, processing time, labor productivity, inventory carrying costs, and transportation expenses. Also consider secondary benefits like improved customer satisfaction, reduced environmental impact, and enhanced ability to respond to market changes. MacMillan Supply Chain Group helps clients establish appropriate metrics and measurement systems to quantify the value of their supply chain investments.

 Creating Strategic Alliances in the Supply Chain
Creating Strategic Alliances in the Supply Chain Our Solutions
Our Solutions